Posted
A survey of 300 cybersecurity professionals who attended a live webinar on cyber risk quantification (CRQ) sponsored by Spire Solutions and ThreatConnect shows that there is truth behind the anecdotal evidence that for too many organizations the early approach to CRQ has been too manual of a process, takes too long, produces questionable results, and has failed to gain the support of business leadership.
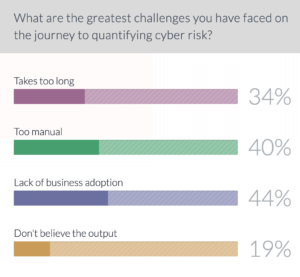
Forty-four percent of attendees said the biggest challenge they’ve faced during their efforts to introduce cyber risk quantification to their overall cybersecurity risk management program has been the lack of business buy-in. That is not surprising given that 40 percent said the manual nature of the cyber risk quantification process was the biggest challenge, and 34 percent said it simply takes too long to show value.
 The results of the informal survey align with years of anecdotal evidence from companies of all sizes that have either attempted to build a CRQ program on their own, or use one of the first generation of software approaches available in the market to do so. But this does not mean that cyber risk quantification isn’t a critically important component of any effective cyber security strategy.
The results of the informal survey align with years of anecdotal evidence from companies of all sizes that have either attempted to build a CRQ program on their own, or use one of the first generation of software approaches available in the market to do so. But this does not mean that cyber risk quantification isn’t a critically important component of any effective cyber security strategy.
“It’s very difficult to see what we’re doing now is actually working or not working because it plays out over a longer timeframe. So that becomes very challenging,” said Osama Salah, a cyber risk quantification expert who works in cybersecurity at UAE government entity. “I think the challenges for implementing [the Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR) standard] or adopting it are very similar to other challenges we have in IT, where you need to change the way work is being done, the way decisions are being done.”
CRQ In Weeks, Not Months
At ThreatConnect, we make cyber risk quantification easy. We have developed a solution that eliminates many of the early pains and pitfalls experienced by early adopters. The CRQ journey is no longer a year of organizational disruption and a massive upfront investment. With ThreatConnect RQ, you can begin to see results and the big picture in a matter of weeks. The proposition for adopting CRQ to chief information security officers (CISOs) can’t be to hire more experts, add more complexity, spend hundreds of thousands of dollars on professional services, and spend a year or more building a system. That’s just an untenable position for most CISOs
At ThreatConnect, our Risk Quantifier solution is designed to drive complexity, time and cost out of the CRQ process. We deliver a decision support system that operates in real time rather than waiting for lengthy interviews, training and manual reviews. It is also supported by a threat intelligence platform (TIP) that injects real-world threat actor analysis into your risk models, and a security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) platform that harnesses the new found ‘north star’ understanding of where to focus and turns that intelligence into action throughout your existing security infrastructure.
Critique Versus Create
Attackers don’t sleep. Nor does your business and its IT infrastructure. With all three functions operating in a hyperdynamic manner, it is not sufficient to take snapshots, or to rely on human calculations. Cyber risk quantification needs to become a decision support system that operates in real time rather than waiting for lengthy interviews, training and manual reviews. This requires automation.
Automated cyber risk quantification is now a reality, and businesses should move quickly to gain a better understanding of their actual business risks and prioritize mitigation efforts so that critical business processes, applications, and data are protected.
The requirement to automate the quantitative process, to map to FAIR but make it better, could not be more urgent. ThreatConnect RQ automates the process, where others don’t. Automation boosts three specific areas for your cyber team:
- Proactively Model and Predict Risk
- Establish a Baseline, Mitigate and Monitor for Changes
- Recommend and Drive Smart Action
Board Reporting
Board-level discussions about cyber risk are increasing the need to identify and quantify cyber risk exposure. Being able to track cyber financial risk over time, understand the impact of budget decisions and ultimately justify spending is now driving business decisions on which risks to tolerate, treat or transfer.
While step one is to understand your organization’s cyber risk exposure in financial terms, the next thing an organization must think about is how to mitigate that risk. ThreatConnect RQ models many different types of attackers and attacks that may infiltrate an organization, as well as an organization’s controls, vulnerability data and critical applications.
RQ’s powerful reporting capability then highlights the risks that are potentially most financially impactful to your organization.
Most RQ customers not only have their controls actively updated in the tool to assess which applications are most vulnerable, but they also provide vulnerability data which allows RQ to provide short-term recommendations on which Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) reduce the most risk by dollar amount.
All of this analysis is then put in a report that business leaders and board members can understand.
Real Math
While the vast majority of approaches to CRQ rely on inputs akin to guesswork, ThreatConnect RQ is transparent and computes risk based on real data.
RQ leverages the industry standard formula for computing risk:
ALE = SLE * ARO
Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE)
Single Loss Expectancy (SLE)
Annual Rate of Occurrence (ARO) = Likelihood * Probability
Data is automatically entered into the RQ Risk Model and Automation Engine. Those inputs include those from your organization’s technical environment as well as industry, attack, and vulnerability data aggregated by ThreatConnect through various sources.
That information is then applied to the risk model and automation engine to determine financial impact of cyber risks and probability of success of specific attacks. These calculations drive a variety of other activities within RQ that lead to operationalization of that information across the rest of your organization, including:
- Prioritization of vulnerabilities not only by CVSS score, but by relevance in terms of financial impact to your business
- ‘What-if’ analysis to help you understand what specific effects certain changes may have on your cyber risk before actually making those changes
- Producing short and long term recommendations on how specific changes may affect ALE and provide guidance into any ‘low hanging fruit’ that may exist
The capabilities of RQ give you a clear picture into inherent and residual risk in a dynamic fashion. Not only is the threat landscape and the parts of it that are relevant to your business changing, but the controls, applications, endpoints, and type of data present in your environment are changing as well. RQ enables you to apply these changes instantaneously to your models, allowing the measurement of cyber risk to move beyond point-in-time assessments and become programmatic in nature.

